Pigmentation: Causes, Types & Best Treatment
Skin is the largest organ of the human body, and Skin health plays a very important role in how we look and feel. One of the most common issues many face is pigmentation. It is a condition where patches of the skin become darker or lighter than the rest of the area. While it is usually harmless but it can affect one’s self-confidence.
In this blog, we will explore what pigmentation is, its types, causes, and effective treatments to get the perfect skin you desire.
What is Pigmentation?
Pigmentation refers to the coloring of the skin, caused by melanin, a pigment produced by specialized skin cells called melanocytes. When melanin production is imbalanced, either too much or too little, it leads to visible skin color changes.
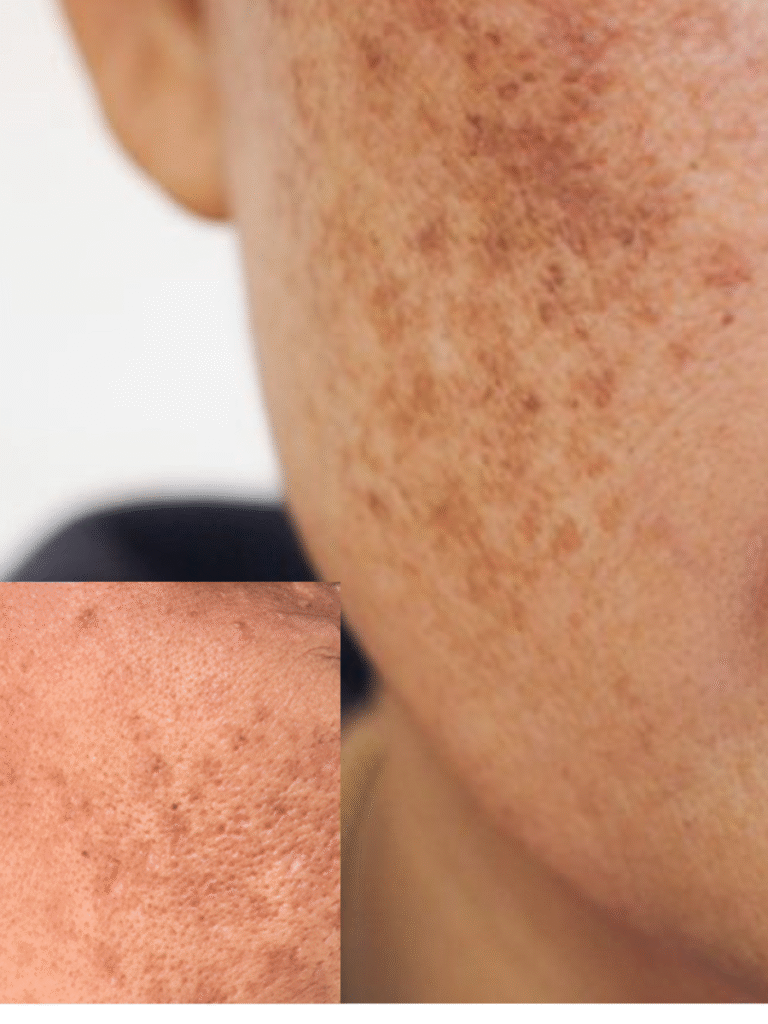
- Hyperpigmentation: Excess production of melanin causes dark patches or spots.
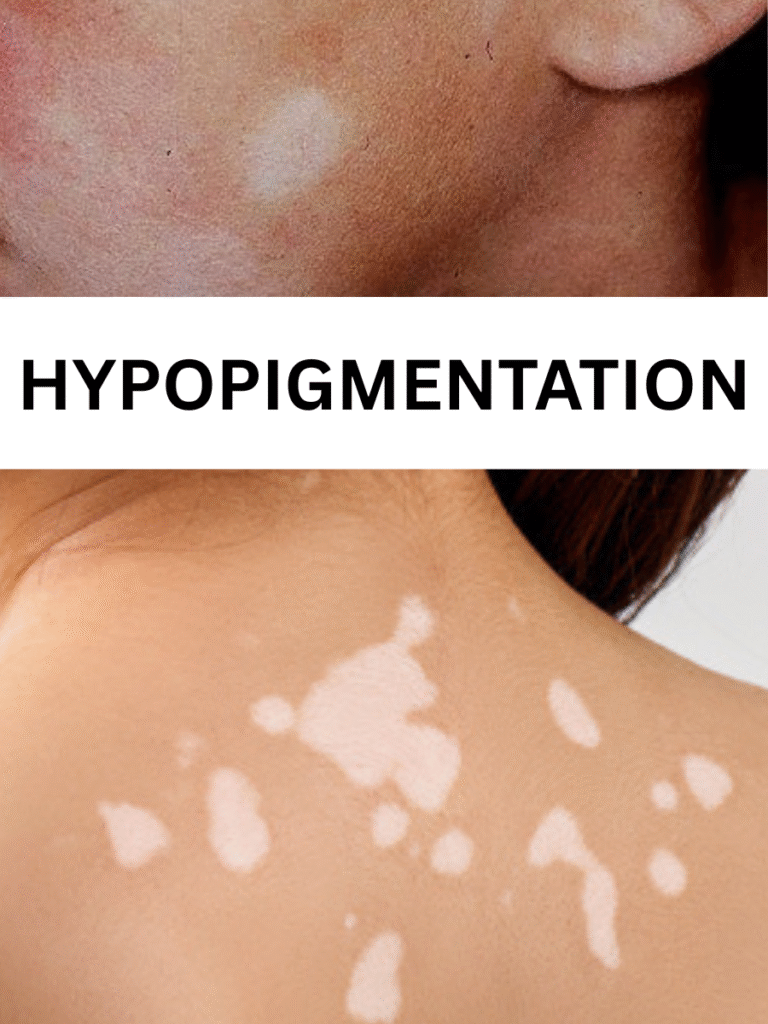
- Hypopigmentation: Reduced melanin production leads to lighter or white patches.
Pigmentation can appear on any part of the body but is most commonly seen on the face, neck, hands, and arms due to sun exposure.
Types of Pigmentation
There are several types of pigmentation, each with different causes and characteristics.
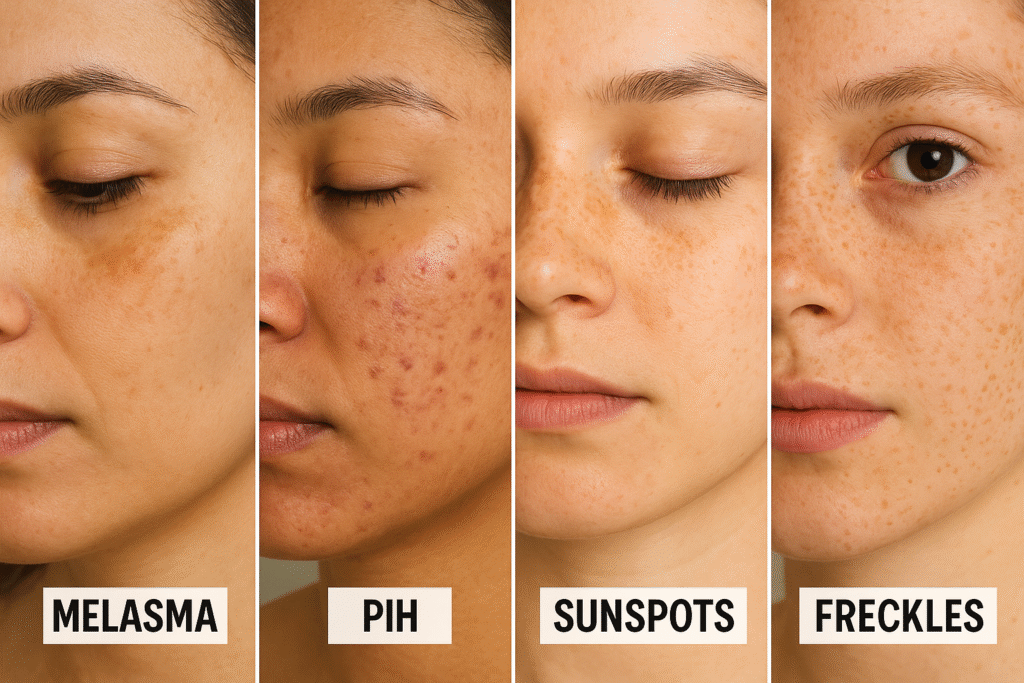

1. Melasma
- Often happens in pregnancy, also called the “mask of pregnancy,” melasma appears as brown or grayish patches, usually on the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip.
- It is more common in women, especially during hormonal changes such as pregnancy or while taking birth control pills.
- Sun exposure tends to make melasma worse.
2. Sunspots (Solar Lentigines)
- These are small, flat, dark spots caused by prolonged sun exposure.
- They are commonly known as age spots or liver spots and often appear on the face, hands, and arms.
- Though harmless, they can make skin appear older.
3. Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
- PIH develops after an injury, acne breakout, burn, or other skin trauma.
- It appears as dark spots or patches where the skin was previously damaged.
- More common in people with medium to dark skin tones. read more about it in this study from the National Institutes of Health.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559150/#:~:text=Postinflammatory%20hyperpigmentation%20results%20from%20overproduction,%2C%20trauma%2C%20or%20dermatologic%20procedures.
4. Freckles
- Small brown spots that usually appear due to sun exposure and genetic factors.
- They are common in people with lighter skin tones and often darken in summer while fading in winter.
5. Vitiligo (Hypopigmentation)
- Unlike the above types, vitiligo is caused by loss of melanin.
- It appears as irregular white patches on the skin.
- It is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks pigment-producing cells.
Causes of Pigmentation
- Excessive Sun Exposure: UV rays directly trigger melanin production, leading to tanning and sunspots.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, thyroid problems, or hormonal medications can cause melasma.
- Skin Inflammation: Acne, eczema, burns, or cuts may leave behind dark spots.
- Genetics: Some pigmentation conditions, like freckles, are inherited.
- Medications: Certain drugs, such as chemotherapy or antibiotics, can trigger pigmentation.
- Aging: With age, melanin distribution becomes uneven, leading to age spots.
Effective Treatments for Pigmentation
Treating it depends on its type, severity, and underlying cause. Here are the most common and effective treatment options:
1. Topical Treatments
- Hydroquinone: A skin-lightening agent often prescribed for melasma and dark spots.
- Retinoids (Retinol, Tretinoin): Promote cell turnover and reduce pigmentation.
- Vitamin C: An antioxidant that brightens skin and reduces melanin formation.
- Niacinamide: Helps lighten dark spots and improves skin texture.
- Azelaic Acid: it is very Useful for treating both acne and pigmentation.
2. Chemical Peels
- Involves applying a chemical solution (like glycolic acid or salicylic acid) to exfoliate the skin.
- Helps in removing the upper layer of damaged skin and lightens pigmentation.
3. Laser Therapy
- Laser treatments target and break down melanin deposits.
- Effective for sunspots, melasma, and PIH but must be done under expert supervision.
4. Microdermabrasion and Dermabrasion
- These procedures exfoliate the top layers of skin using fine crystals or a rotating device.
- Improve skin tone and reduce pigmentation gradually.
5. Cryotherapy
- Involves freezing pigmented areas with liquid nitrogen.
- Commonly used for sunspots and age spots.
Cryotherapy is an effective treatment for sunspots, supported by clinical studies.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9455088
6. Home Remedies (Supportive Care)
While medical treatments are more effective, some natural remedies can help manage mild pigmentation:
- Aloe Vera Gel: aloevera Soothes and lightens dark spots.
- Green Tea Extract: It has anti-inflammatory properties which can reduce the spots.
- Turmeric: It contains curcumin, which helps regulate melanin production.
- Kojic Acid: kojic acid is derived from a fungus, is a common and effective natural-lightening agent. it is a by-product of fermented rice and is very effective at reducing melanin production. In many professional skincare products for treating hyperpigmentation, kojic acid is a key ingredient.
Preventing Pigmentation
Prevention is key to managing the issues. Here are some tips:
- Always Wear Sunscreen: Broad-spectrum SPF 50 or higher, reapplied every 2-3 hours.
- Protective Clothing: Hats, sunglasses, and full-sleeved clothes for sun protection.
- Avoid Picking at Skin: Popping pimples or scratching injuries can worsen the spots.
- Healthy Diet: Foods rich in antioxidants (fruits, vegetables, nuts) can help protect skin.
- Hydration & Skincare: Gentle cleansing and moisturizing to maintain a healthy skin barrier.
Final Thoughts
Pigmentation is a common skin issue that affects people of all ages and skin types. While it is usually harmless, it can impact one’s appearance and confidence. Understanding the type and seeking the right treatment can help achieve clearer, healthier skin.
If you struggle with persistent pigmentation, consulting a dermatologist is the best way to identify the underlying cause and find the most effective treatment plan for your skin.
Remember, beautiful skin isn’t about being flawless, but about being healthy and cared for.


1 comment